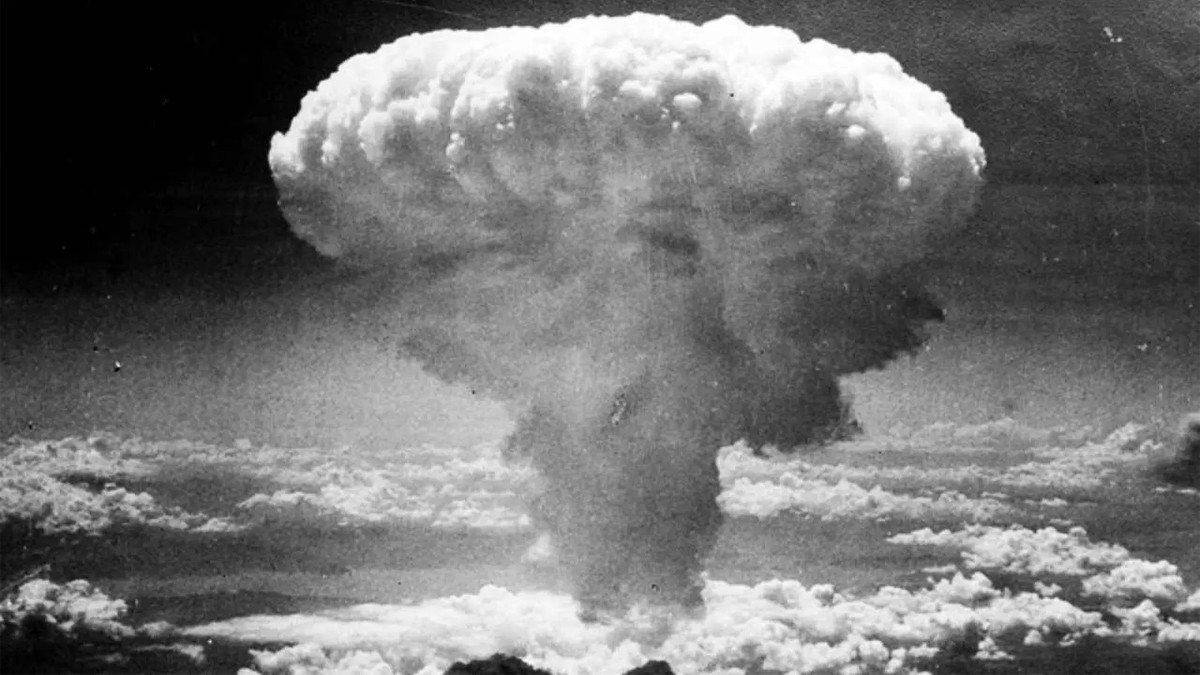
On August 9, 1945, a second atom bomb named 'Fat Man' was dropped on Japan by the United States, at Nagasaki.
This came after three days Hiroshima was devastated by the first uranium bomb, coded 'Little Boy', on August 6, leaving over 74,000 people dead.
Japan was still trying to recover from the shock of the first atom bombing at Hiroshima on August 6. Just three days after, it was again shaken by another nuclear bombing in Nagasaki by the United States.
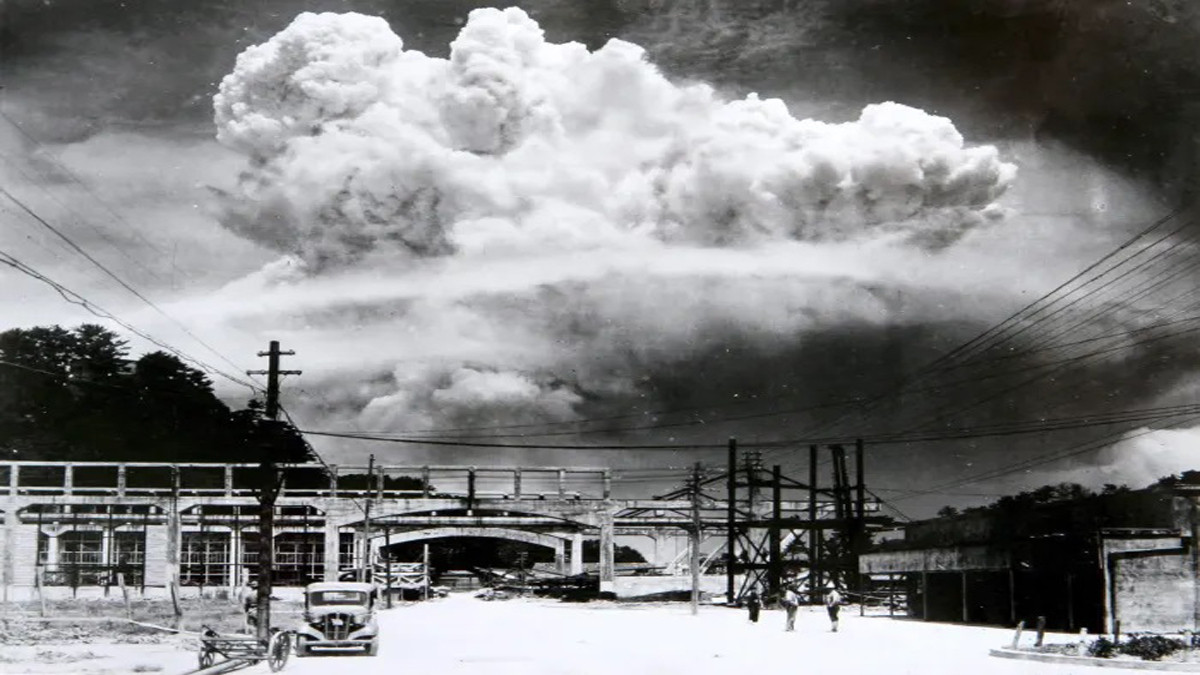
The 4.5-ton plutonium bomb code name 'Fat Man' was dropped at 11.02 am on August 9, 1945, by the US B029 bomber Bockscar. When the bomb hit the ground, the temperature of the surface reached 4,000 degrees Celsius, and radioactive rain poured down.
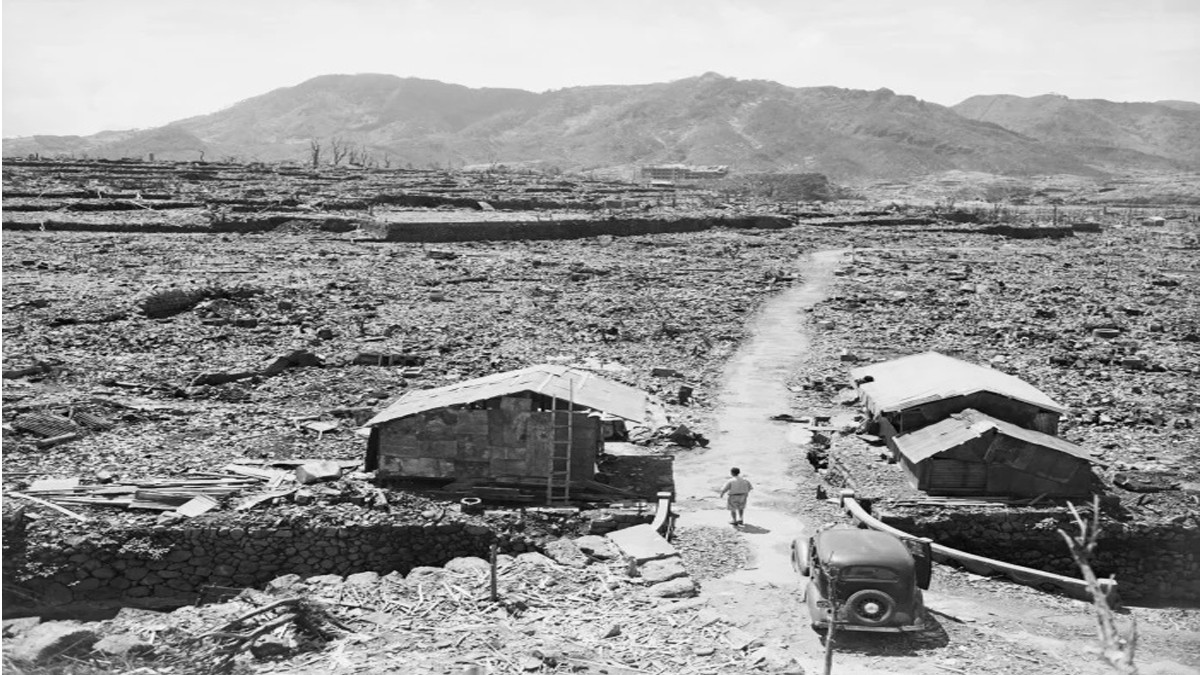

This attack forced Japan to an unconditional surrender during the Second World War. After six days of the Nagasaki bombing, the Japanese Emperor Gyokuon-Hoso's speech was broadcast to the nation, addressing the surrender. Both the bombings claimed the lives of over 140,000 people out of the total estimated population of 3.5 lakh. Later, the death toll kept rising due to injuries and radiation-related deaths.
The bomb named 'Fat Man', which destroyed the city of Nagasaki was more powerful than the bomb 'Little Boy' used in Hiroshima.
Numerous hospitals in Nagasaki were completely destroyed, the majority of the city's doctors and nurses died or were severely injured, and countless individuals experienced major injuries. The majority of victims perished without receiving any treatment to ease their pain. Some of those who entered the city after the bombings also died due to radiation.

Even five to ten years after the bombings, the survivors began suffering from several other diseases like thyroid, breast, lung, and other cancers at higher than normal rates. Pregnant women who were exposed to the bombing had a higher rate of miscarriage and infant death. And the children who were exposed to the radiation in their mother's womb experienced intellectual disabilities, impaired growth, and also increased rates of developing cancer.